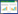金属已成为现代生产生活中必不可少的材料,具有广泛的应用。在金属的生产、加工、应用过程中普遍伴随着金属腐蚀,金属腐蚀破坏了金属的优良性能,严重限制了金属的应用,造成重大的经济损失[1-3]。在发达国家每年由于腐蚀引起的经济损失大约占国民生产总值的3.5%~4.2% [4]。因此,采取有效的金属防护方法势在必行。
自1977年Shirakawa、MacDiamid与Heeger发现导电聚合物以来,导电聚合物受到了众多研究者的关注,现已应用于各个领域,例如:超级电容器[5]、生物传感器[6]、二次电池[7]与金属防腐[8]等。由于其生产工艺简单、稳定性好、导电率高,聚苯胺(polyaniline,PANI)是研究最多的导电聚合物之一。聚苯胺是由“苯-苯”相连的还原单元与“苯-醌”相连的氧化单元交替出现构成的线型高分子[9],其结构如图 1所示。
|
| 图 1 聚苯胺分子结构式 Figure 1 The molecular structure of PANI |
| |
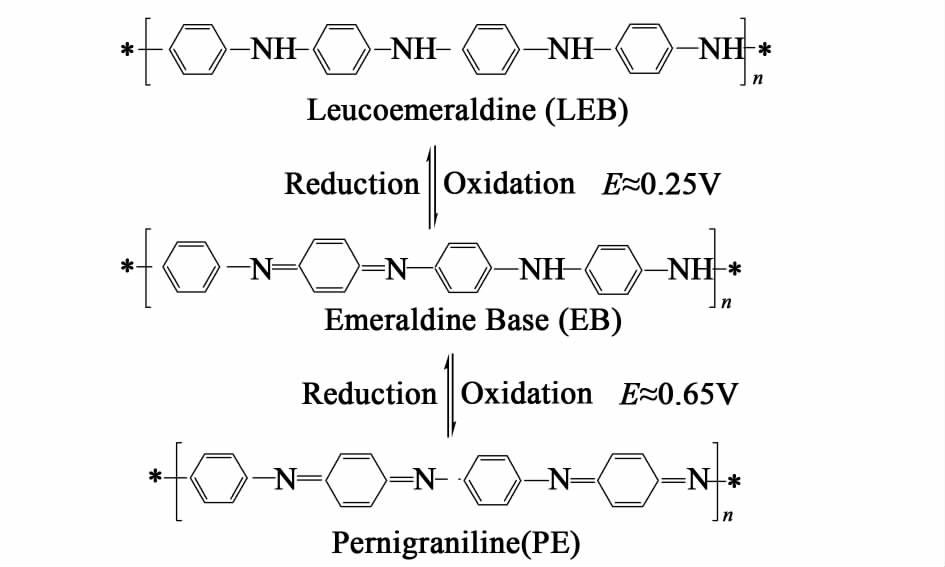
在图 1中,n表示结构单元数,即聚合度;y(0≤y≤1)为聚苯胺的还原程度。随着y值的的变化,聚苯胺呈现不同的氧化状态,当y=1.0时,聚苯胺为全苯式完全还原态;当y=0.5时,聚苯胺为还原单元数与氧化单元数相等的半氧化态;当y=0时,聚苯胺为苯-醌交替的完全氧化态,这3种氧化态之间是可以相互转化的,如图 2所示。
|
| 图 2 聚苯胺的氧化还原过程 Figure 2 The redox process of PANI |
| |
大量研究表明聚苯胺可以用于金属防腐,并提出了多种聚苯胺防腐机理,其中被大家所认可的防腐机理主要有以下3种。
1.1 屏蔽作用[10-11]当聚苯胺作为涂层涂覆于金属表面时,可作为屏蔽层有效地将金属与腐蚀介质隔绝开,起到保护金属的作用。Beck[12]曾研究电化学法合成聚苯胺对金属基材的防腐作用,研究结果表明聚苯胺涂层厚度只有超过1 μm才具有防腐性能。因此,聚苯胺涂层的物理屏蔽是聚苯胺具有防腐性能的基础。
1.2 钝化金属机理[13]聚苯胺可促使在涂层/金属基材界面上生成一层致密的金属氧化层,使金属处于钝化状态。致密钝化层的生成使聚苯胺具有抗点蚀、抗划伤等优异的防腐性能。聚苯胺通过在不同氧化态之间的转化,促进对金属的钝化作用。当处于一定氧化状态的聚苯胺与钢铁接触时,聚苯胺能够促使铁表面上致密氧化层Fe3O4生成,其自身被还原,随后空气或溶液中的氧再氧化聚苯胺提高其氧化态,其过程如图 3所示。

|
| 图 3 聚苯胺对铁的钝化机理 Figure 3 The passivation mechanism of PANI towards steel |
| |
聚苯胺自身可进行氧化还原反应,聚苯胺能够使金属基材的氧化电位上升,将金属的氧化电位稳定在钝化区,大幅度地降低了金属的溶解速率,对金属起到了保护作用。
2 聚苯胺的防腐方式聚苯胺可有效地防止金属腐蚀,主要通过3种方式应用于防腐:缓蚀剂、聚苯胺涂层与复合涂层的添加剂。
2.1 缓蚀剂缓蚀剂是指向腐蚀介质中加入少量即可有效抑制或防止金属腐蚀的一类物质,其分子结构中常含有氮(N)、硫(S)与氧(O)等电负性较大且可提供孤电子对的原子。在腐蚀环境中,缓蚀剂能取代水分或腐蚀离子吸附于金属表面,使金属与腐蚀环境隔绝开,起到抑制金属腐蚀的目的。因此,缓蚀剂防腐性能的强弱主要取决于缓蚀剂在金属表面的吸附强度。缓蚀剂在金属表面吸附强度的主要影响因素有:1)缓蚀剂的分子结构(包括立体结构);2)缓蚀剂的芳香性、供体的电荷密度;3)其它功能基团的性质;4)分子的面积(分子的形状与相对分子质量)。此外,在缓蚀剂分子中,官能团NH、—NN—、—CHO、R—OH与RR等的存在可有效提高缓蚀剂在金属表面的吸附强度。缓蚀剂的优点是使用方便,可以应用于形状复杂管道等的防护;缺点是形成的防护层较薄且常有缺陷。因此,与常规的涂层相比,缓蚀剂的防腐效率较低。
聚苯胺分子结构中含有多个可提供孤对电子对的氮原子,能与金属原子中空的d轨道形成配位键,增强聚苯胺与金属之间的相互作用力,使聚苯胺在金属上的黏附力增强;聚苯胺相对分子质量大,提高了聚苯胺在金属表面的覆盖率。因此,聚苯胺可作为缓蚀剂有效地保护金属。众多研究者利用Tafel曲线对聚苯胺缓蚀剂防腐性能进行考察,结果显示腐蚀电流(icorr)急剧下降,腐蚀电位(Ecorr)变化较小,表明聚苯胺属于混合型缓蚀剂[16]。Jeyaprabha等研究了聚苯胺的衍生物聚胺醌缓蚀剂,发现该缓蚀剂不仅可以吸附于金属表面保护金属,还可以钝化金属,进一步对金属起到保护作用[17]。
聚苯胺高分子链之间存在氢键、电性力及π-π作用力,分子间作用力强。因此,聚苯胺是一种溶解度很小的导电聚合物,这严重限制了其在缓蚀剂中的应用。提高聚苯胺溶解性的方法有:1)使用聚苯胺纳米材料[18]或使用表面活性剂[19];2)使用聚苯胺衍生物,以减小分子间的相互作用力。当衍生物带有亲水基团时,更能显著提高聚苯胺的溶解性。聚苯胺衍生物还可以提高相对分子质量和分子尺寸,有利于提高其在金属表面的覆盖率,提高缓蚀效率。常见的可溶性聚苯胺衍生物有:聚二苯基胺[20](10×10-6时,缓蚀效率达96%)、聚胺醌[17](1 000×10-6时,缓蚀效率可达91%)、聚苯胺-甲醛[21](10×10-6时,缓蚀效率约为94%)与聚邻氨基苯甲酸[22](60 mg/L时,缓蚀效率约为94%)等;3)降低聚苯胺的相对分子质量,以降低聚苯胺高分子链间的作用力与缠绕程度,提高其溶解性[23]。这种方法的缺点是降低了聚苯胺在金属表面的覆盖率,可能会降低缓蚀效率。与高相对分子质量聚苯胺不同,苯胺低聚体主要抑制阳极腐蚀,其缓蚀效率主要取决于低聚体分子链的长度与低聚体上官能团的位置;4)苯胺与其他苯胺衍生物共聚[24-25],打乱聚苯胺高分子链的有序性,降低分子间作用力,提高其溶解性。
2.2 聚苯胺涂层与聚苯胺缓蚀剂相比,聚苯胺涂层解决了聚苯胺溶解性小这一难题,应用更广泛。聚苯胺涂层可以作为物理屏蔽层,有效地把金属与腐蚀环境隔离开,保护金属基材。大量研究表明聚苯胺还可以在涂层/金属基材界面上诱导生成致密的金属氧化物,钝化金属基材,进一步保护金属。
聚苯胺涂层主要通过电化学聚合法直接将聚苯胺沉积在金属基材表面。聚苯胺合成与在金属上成膜一次完成,制备工艺简单且成本低廉,可以在复杂界面上沉积成膜。电化学合成聚苯胺涂层有以下特点:1)电化学法合成聚苯胺的方法多样,有恒电位法[26]、恒电流法[27-28]、循环伏安法[29]等,且影响因素较多,生成的聚苯胺膜的性质不稳定;2)聚苯胺需在高电位聚合,其性质受金属基材的影响,限制了金属基材的种类[30];3)电化学法合成聚苯胺涂层很难用于较大的金属基材,很难大规模应用,对金属基材结构与大小有要求;4)电化学法生成的聚苯胺涂层孔隙率较大;5)聚苯胺的氧化还原过程(掺杂/脱掺杂过程)伴随着对阴离子的进入和脱出,对阴离子从聚苯胺涂层中脱出会导致涂层的孔隙率提高,提高了腐蚀介质在聚苯胺膜中的传质速度,使涂层防护效率下降。随着掺杂离子的掺杂/脱掺杂,聚苯胺涂层还会发生较大的体积膨胀/收缩,这一过程中会产生很大的界面应力,导致涂层在金属材料表面的附着力降低,有时甚至剥落;6)电化学合成聚苯胺一般在水溶液中进行,制得的聚苯胺涂层中含有较多的水分,致密度较低,在干燥过程中,经常出现涂层龟裂现象;7)电沉积聚苯胺涂层只在最接近金属基材表面能形成致密涂层,之后的涂层疏松、致密性差。因此,涂层厚度的增加对涂层防腐性能的改善较小。这些缺点限制了聚苯胺涂层的大规模化,适用于小批量生产。但是电化学法制得的聚苯胺涂层纯度高,其防腐体系与机理较简单。因此,电化学法合成聚苯胺涂层常用于理论研究,考察聚苯胺的防腐机理。
导电聚合物涂层还可以通过溶解法制得[31-32]。溶解法是指将聚苯胺溶于溶剂中,之后将其涂覆于金属基材上,待溶剂挥发后形成涂层。溶解法对金属基材没有要求,但是制得的聚苯胺涂层附着力差。聚苯胺在一般溶剂中溶解性均很差,可溶解聚苯胺的溶剂价格昂贵、且毒性大。因此,在聚苯胺防腐应用中,很少使用溶解法。
2.3 聚苯胺复合涂层聚苯胺溶解性差、附着力较差、致密性差且成本比一般有机涂层高很多。为克服这些缺点可将已制得的聚苯胺与树脂复合制备聚苯胺复合涂层。聚苯胺复合涂层附着力好、防腐性能佳且成本低。因此,与缓蚀剂、聚苯胺涂层相比,聚苯胺复合涂层应用最为广泛。一般将含量少于3.0%的聚苯胺以物理混合的方式均匀地分散于有机涂层中,制得聚苯胺复合涂层。
有机涂层作为物理屏蔽层可有效地使涂层与腐蚀环境隔绝开,但长期在腐蚀环境下,有机涂层的机械性能、致密性与防腐性能均会下降。为使涂层能够长期有效地具有优异防腐性能,常向涂层中添加一些无机添加剂钝化金属,这些无机添加剂常为铬与铅等重金属盐类,具有毒性与致癌性,对人体与环境具有严重的危害。聚苯胺为环境友好型导电聚合物,稳定性好、具有独特的防腐机制,能够取代重金属作为有机涂层的添加剂制备聚苯胺复合涂层,增强涂层的防腐性能。常见的聚苯胺复合涂层有聚苯胺/环氧树脂[33-34]、聚苯胺/聚氨酯[35-36]、聚苯胺/丙烯酸酯[37]与聚苯胺/醇酸树脂[38-39]涂层等。大量文献报道表明聚苯胺复合涂层可以对金属基材起到长期有效的保护作用,Chen等[33]研制的聚苯胺/环氧树脂涂层可在室温下3.5% NaCl溶液中保持优异的防腐性能达150 d。然而,在聚苯胺复合涂料中常出现聚苯胺团聚或分散不均一等现象,大幅度地降低了涂层的致密性,使涂层的防腐性能下降[40-41]。因此,在聚苯胺复合涂层中解决聚苯胺在有机涂层中的分散性是关键。
3 结论与展望1) 聚苯胺具有环境友好性、良好的环境稳定性、抗划伤与抗点蚀性,可以在涂层/金属基材界面上诱导生成致密的金属氧化层,钝化金属,在防腐领域具有广阔的应用前景。
2) 聚苯胺可作为缓蚀剂抑制或防止金属腐蚀,聚苯胺缓蚀剂可以应用于结构复杂管道的防腐,但是因吸附形成的防护层较薄,存在缺陷,缓蚀效果较弱。聚苯胺的溶解性小严重限制了该应用,虽然改善聚苯胺溶解性的方法有很多,但溶解性仍较小,需进一步对聚苯胺的溶解性进行改善,使聚苯胺作为缓蚀剂的应用更加广泛。
3) 聚苯胺涂层解决了聚苯胺溶解性差这一问题,但电化学法合成聚苯胺涂层无法大规模应用且致密性差,溶解法制得的聚苯胺涂层附着力差且成本很高。因此,与聚苯胺复合涂层相比,聚苯胺涂层防腐性能较差,且成本高,很难大规模生产、应用。但是,电化学法合成的聚苯胺涂层纯度高,防腐体系及机理较简单,对研究、分析聚苯胺的防腐机理有重要的意义。
4) 聚苯胺复合涂层具有很好的防腐性能、无毒无害,成本低,应用最为广泛。但聚苯胺分散性较差是一难题,聚苯胺分散性得以改善将会大幅度地提高聚苯胺复合涂层的防腐性能。
聚苯胺的防腐研究现主要集中于钢铁上,其他金属基材的防腐研究较少。可以进一步拓展到其他金属,例如镁、铝、及其合金等。
| [1] | Yang T, Peng C, Lin Y, et al. Synergistic effect of electroactivity and hydrophobicity on the anticorrosion property of room-temperature-cured epoxy coatings with multi-scale structures mimicking the surface of Xanthosoma sagittifolium leaf[J]. J Mater Chem,2012,22 (31) : 15845–15852 |
| [2] | Jang J, Kim E K. Corrosion protection of epoxy-coated steel using different silane coupling agents[J]. J Appl Polym Sci,1999,71 (4) : 585–593 |
| [3] | Zhao Y, Zhang W, Liao L, et al. Self-Healing coatings containing microcapsule[J]. Appl Surf Sci,2012,258 (6) : 1915–1918 |
| [4] | 叶康民. 金属腐蚀与防护概论[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 1980 |
| [5] | Wang H, Hao Q, Yang X, et al. Graphene oxide doped polyaniline for supercapacitors[J]. Electrochem Commun,2009 : 1158–1161 |
| [6] | Xian Y, Hu Y, Liu F, et al. Glucose biosensor based on Au nanoparticles-conductive polyaniline nanocomposite[J]. Biosens Bioelectron,2006 : 1996–2000 |
| [7] | Ryn K S, Kim K M, Kang S G, et al. Electrochemical and physical characterization of lithium ionic salt doped polyaniline as a polymer electrode of lithium secondary battery[J]. Synth Met,2000 : 213–217 |
| [8] | Armelin E, Pla R, Liesa F, et al. Corrosion protection with polyaniline and polypyrrole as anticorrosive additives for epoxy paint[J]. Corros Sci,2008,50 (3) : 721–728 |
| [9] | Macdiarmid A G, Chiang J C, Richter A F. Polyaniline: A new concept in conducting polymers[J]. Synth Met,1987,18 (1/3) : 285–290 |
| [10] | Wessling D B. Passivation of metals by coating with polyaniline: Corrosion potential shift and morphological changes[J]. Adv Mater,1994,6 (3) : 226–228 |
| [11] | 马利, 杨桔, 王成章. 复合型聚苯胺防腐涂料的研究进展[J]. 表面技术,2006,35 (2) : 7–9 Ma Li, Yang Ju, Wang Chengzhang. Research progress on compound anticorrosion coatings of polyaniline[J]. Surface Technology,2006,35 (2) : 7–9 |
| [12] | 邓宇强, 葛岭梅, 周安宁. 聚苯胺防腐蚀涂料的研究进展[J]. 腐蚀与防护,2003,24 (8) : 333–336 Deng Yuqiang, Ge Lingmei, Zhou Anning. Development of the research in polyaniline anti-corrosion coatings[J]. Corrosion & Protection,2003,24 (8) : 333–336 |
| [13] | Rohwerder M, Michalik A. Conducting polymers for corrosion protection: What makes the difference between failure and success?[J]. Electrochim Acta,2007,53 (3) : 1300–1313 |
| [14] | Sathiyanarayanan S, Karpakam V, Kamaraj K, et al. Sulphonate doped polyaniline containing coatings for corrosion protection of iron[J]. Surf Coat Technol,2010,204 (9/10) : 1426–1431 |
| [15] | Sathiyanarayanan S, Jeyaram R, Muthukrishnan S, et al. Corrosion protection mechanism of polyaniline blended organic coating on steel[J]. J Electrochem Soc,2009,156 (4) : C127–C134 |
| [16] | Jeyaprabha C, Sathiyanarayanan S, Venkatachari G. Effect of cerium ions on corrosion inhibition of PANI for iron in 0.5 M H2SO4[J]. Appl Surf Sci,2006,253 (2) : 432–438 |
| [17] | Jeyaprabha C, Sathiyanarayanan S, Phani K L N, et al. Influence of poly(aminoquinone) on corrosion inhibition of iron in acid media[J]. Appl Surf Sci,2005,252 (4) : 966–975 |
| [18] | Yao B, Wang G, Ye J, et al. Corrosion inhibition of carbon steel by polyaniline nanofibers[J]. Mater Lett,2008,62 (12/13) : 1775–1778 |
| [19] | Liu L, Levon K. Undoped polyaniline-surfactant complex for corrosion prevention[J]. J Appl Polym Sci,1999,73 (14) : 2849–2856 |
| [20] | Jeyaprabha C, Sathiyanarayanan S, Phani K L N, et al. Investigation of the inhibitive effect of poly(diphenylamine) on corrosion of iron in 0.5 M H2SO4 solutions[J]. J Electroanal Chem,2005,585 (2) : 250–255 |
| [21] | Quraishi M A, Shukla S K. Poly(aniline-formaldehyde): A new and effective corrosion inhibitor for mild steel in hydrochloric acid[J]. Mater Chem Phys,2009,113 (2/3) : 685–689 |
| [22] | Shukla S K, Quraishi M A, Prakash R. A self doped conducting polymer "polyanthranilic acid": An efficient corrosion inhibitor for mild steel in acidic solution[J]. Corros Sci,2008,50 (10) : 2867–2872 |
| [23] | Yadav D K, Chauhan D S, Ahmad I, et al. Electrochemical behavior of steel/acid interface: Adsorption and inhibition effect of oligomeric aniline[J]. RSC Adv,2013 : 632–646 |
| [24] | Bhandari H, Choudhary V, Dhawan S K. Synergistic effect of copolymers composition on the electrochemical, thermal, and electrical behavior of 5-lithiosulphoisophthalic acid doped poly(aniline-co-2-isopropylaniline): Synthesis, characterization, and applications[J]. Polym Adv Technol,2009,20 (12) : 1024–1034 |
| [25] | Benchikh A, Aitout R, Makhloufi L, et al. Soluble conducting poly(aniline-co-orthotoluidine) copolymer as corrosion inhibitor for carbon steel in 3% NaCl solution[J]. Desalination,2009,249 (2) : 466–474 |
| [26] | Wang T, Tan Y. Understanding electrodeposition of polyaniline coatings for corrosion prevention applications using the wire beam electrode method[J]. Corros Sci,2006,48 (8) : 2274–2290 |
| [27] | Nooshabadi M S, Ghoreishi S M, Behpour M. Electropolymerized polyaniline coatings on aluminum alloy 3004 and their corrosion protection performance[J]. Electrochim Acta,2009,54 (27) : 6989–6995 |
| [28] | Tan C, Blackwood D J. Corrosion protection by multilayered conducting polymer coatings[J]. Corros Sci,2003,45 (3) : 545–557 |
| [29] | Fang J, Xu K, Zhu L, et al. A study on mechanism of corrosion protection of polyaniline coating and its failure[J]. Corros Sci,2007,49 (11) : 4232–4242 |
| [30] | Kraljic M, Mandic Z, Duic L. Inhibition of steel corrosion by polyaniline coatings[J]. Corros Sci,2003,45 (1) : 181–198 |
| [31] | Cecchetto L, Ambat R, Davenport A J, et al. Emeraldine base as corrosion protective layer on aluminium alloy AA5182, effect of the surface microstructure[J]. Corros Sci,2007,49 (2) : 818–829 |
| [32] | Shreepathi S, Hoang H V, Holze R. Corrosion protection performance and spectroscopic investigations of soluble conducting polyaniline-dodecylbenzenesulfonate synthesized via inverse emulsion procedure[J]. J Electrochem Soc,2007,154 (2) : C67–C73 |
| [33] | Chen Y, Wang X, Li J, et al. Long-Term anticorrosion behaviour of polyaniline on mild steel[J]. Corros Sci,2007,49 (7) : 3052–3063 |
| [34] | Armelin E, Oliver R, Liesa F, et al. Marine paint formulations: Conducting polymers as anticorrosive additives[J]. Prog Org Coat,2007,59 (1) : 46–52 |
| [35] | Riaz U, Ahmad S A, Ashraf S M, et al. Effect of dopant on the corrosion protective performance of environmentally benign nanostructured conducting composite coatings[J]. Prog Org Coat,2009,65 (3) : 405–409 |
| [36] | Peng C, Hsu C H, Lin K, et al. Electrochemical corrosion protection studies of aniline-capped aniline trimer-based electroactive polyurethane coatings[J]. Electrochim Acta,2011 : 614–620 |
| [37] | Souza S D. Smart coating based on polyaniline acrylic blend for corrosion protection of different metals[J]. Surf Coat Technol,2007,201 (16/17) : 7574–7581 |
| [38] | Alam J, Riaz U, Ahmad S. High performance corrosion resistant polyaniline/alkyl ecofriendly coatings[J]. Curr Appl Phys,2009,9 (1) : 80–86 |
| [39] | Jadhav R S, Hundiwale D G, Mahulikar P M. Synthesis of nano polyaniline and poly-o-anisidine and applications in alkyd paint formulation to enhance the corrosion resistivity of mild steel[J]. J Coat Technol Res,2010,7 (4) : 449–454 |
| [40] | 刘军喜, 苏光耀, 高德淑, 等. 聚苯胺防腐涂料的制备与性能研究[J]. 表面技术,2005,34 (1) : 50–52 Liu Junxi, Su Guangyao, Gao Deshu, et al. Preparation and property research of polyaniline anticorrosive coating[J]. Surface Technology,2005,34 (1) : 50–52 |
| [41] | 卢华军, 曾波. 聚苯胺防腐涂料的研究现状及发展[J]. 涂料工业,2007,37 (1) : 50–54 Lu Huajun, Zeng Bo. Current status of development of polyaniline corrosion protective coating[J]. Paint & Coatings Industry,2007,37 (1) : 50–54 |
 2016, Vol. 33
2016, Vol. 33