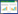2. 中国科学院过程工程研究所, 北京 100190
2. Institute of Process Engineering, Chinese Academy of Science, Beijing 100190, China
结晶是很多工业操作必不可少的一个分离和纯化单元,由于结晶操作能耗低,晶体产品纯度高并且易于储存和运输,结晶在医药、化工、生物和材料等领域都有非常广泛的应用。
结晶是相变过程,是固体物质从溶液(气相或液相)或熔融状态下以晶体形式析出的过程,其推动力主要来自于结晶系统在热力学上的非平衡特性,即溶质在液相和固相化学势的差值[1]。因此,在对某个体系的结晶过程进行研究时,首先要确定该体系在特定条件下的热力学性质。溶解度等热力学性质可以帮助计算该结晶过程收率的理论极限,同时,结晶过程的热力学数据能够为后续结晶动力学和工艺优化提供理论指导[2]。
结晶的第1步是产生晶核,能否形成晶核取决于相变进行的方向。根据热力学原理,在1个体系内,凡可以自发进行的过程都是吉布斯自由能减小的过程。溶液在形成能稳定存在的最小尺寸的晶核时,总的自由能会达到最大值,进一步的结晶过程导致自由能的减少,这时晶核就会自然长大[3]。成核又分为初级成核和二次成核。初级均相成核是指在纯净均相的过饱和溶液中自发产生晶核的过程,而二次成核则是在含有该晶体的过饱和溶液中发生的成核。晶核出现之后就开始长大即晶体生长过程,生长机理包括表面能理论[4]、二维成核理论[5]和吸附反应理论[6]等各种理论。生长过程中还可能存在晶型的转变、晶习的改变等现象,这些都受到温度、溶剂和杂质等各种因素的影响。以上现象与溶液的热力学性质有着很大的关系,所以结晶热力学方面的研究能够帮助我们对于这些现象的深入认识和调控提供指导。
1 溶解度测定和模拟 1.1 溶解度测定溶解度是非常重要的热力学性质,它是确定介稳区宽度和计算过饱和度的前提,是结晶过程设计和优化的依据。固体溶解度的测量方法一般分为静态法和动态法[7]。
静态法是在一定条件下加入过量的溶质充分搅拌,在等待时间足够后,取体系溶液过滤后采用称重法、分光光度计法或者液相色谱法等测定溶质饱和浓度。张婵等[8]使用静态法测量了AlCl3 ·C6H2O在不同体系中的溶解度,实验表明离子色谱法在测定溶解度数据的方法中是比较准确的。Li等[9]采用静态法测量了NaBr-SrBr2-H2O和KBr-SrBr2-H2O体系的溶解度,浓度数据由折射率法测定。静态法具有重复性好、准确度较高的特点。然而对于具有多晶型的体系,在测定介稳晶型溶解度时,如果溶液介导转晶速率比较快,则不适宜采用静态法测定。
动态法又分为固定温度和改变温度2类,固定温度的测量方法是在特定温度下少量多次加入已知量的溶质,直至不再溶解为止,根据所加入溶质总量可以计算该温度下饱和浓度即溶解度;改变温度的测量方法是在体系中加入稍过量的溶质,缓慢调整溶液温度直至刚好完全溶解,此时的温度即为溶解平衡温度。动态法中溶解终点的判定是关键。目前有各种方式确定终点,传统方法通过目测、浊度仪、激光法等判断终点。比如王海蓉等[10]采用激光法测定了赤藓糖醇在水中的溶解度,通过激光强度的变化判定溶解终点。随着过程分析技术的发展,越来越多的在线浓度或粒度监测设备用于溶解终点的判定。静态法适用于溶解度小的体系,动态法对于溶解度较大的体系更为准确,2种方法的应用都非常广泛[11]。
1.2 溶解度拟合获取溶解度实验数据后,可以采用理论模型或者经验方程,对溶解度数据进行拟合,进而检验溶解度数据的准确性并作为溶解度预测的依据。溶解度拟合方法包括简化模型法、活度系数法、拓扑法、状态方程法和人工神经网络法等[12],表 1总结了部分较为常用的溶解度预测模型的优缺点。目前使用较多的理论模型包括修正后的Apelblat方程和λh[13]等。梁玺等[14]采用Apelblat方程拟合了葡萄糖酸钙的溶解度和超溶解度曲线,得到了葡萄糖酸钙的介稳区宽度,为工业结晶的放大提供了理论基础。刘珏欣等[15]采用了Apelblat方程关联了磷酸二氢钾的热力学数据,优化了工业生产中蒸发结晶的参数,制备出高质量的磷酸二氢钾产品。此外,基于局部组成理论的NRTL模型和UNIFAC模型等,是溶解度模拟中常用的活度系数模型,在中低温下的非极性体系中预测精度较高。房彬彬等[16]利用Apelblat方程和NRTL模型计算出混合体系的热力学参数,探究了二苯甲酮混合和溶解过程的自发性。Jolliffe等[17]将NRTL模型应用到青蒿素结晶过程中,成功分析了3种反溶剂对其潜在影响。Wilson模型也是活度系数法的一种,使用的二元交互参数受温度影响较小,也常用来作为溶解度的预测模型[18]。
| 溶解度模型 | 类型 | 优势 | 局限性 |
| Apelblat方程 | 经验模型 | 适用范围广,适应性强。 | 模型简单,对随温度变化较大的体系预测结果偏差大。 |
| λh方程 | 经验模型 | 处理方便,对于非极性体系的预测值精度较高,有物质的熔点即可进行回归。 | 对于极性较强的体系不在适用。 |
| Wilson模型 | 活度系数模型 | 二元交互参数受温度影响小,用二元体系数据可以预测多元体系。 | 不能应用于液相分层的体系。 |
| UNIFAC模型 | 活度系数模型 | 适应于中低温度下的非极性体系,可以预测非电解质在溶液中的溶解度,精度较高。 | 对于极性太强的或高温环境下的体系不适用。 |
| NRTL模型 | 活度系数模型 | 适用范围广,计算准确度较高,可以用于极性或非极性体系。 | 参数较多,一般仅用于非电解质体系。 |
| e-NRTL模型 | 活度系数模型 | 适用各种含有电解质溶液体系,精度高,对部分互溶体系也有较好的预测效果。 | 参数较多,回归较麻烦,存在电离平衡的体系关联比较复杂。 |
对于电解质溶液体系,目前已在Debye-Hackel理论的基础上发展出了Bromley方程[19]、Meissner方程[20]、Pitzer模型[21]、e-NRTL方程等[19-23]。近年来,OLI公司又开发出了适用于混合电解质体系的MSE模型[24]。对于电解质溶液的活度系数计算,MSE模型和e-NRTL方程都是非常精确的。Zhang等[25]使用MSE模型计算出Mg-Na-Cl-CO3-CO2-MEG-H2O体系溶解度,计算结果与实验结果都非常的吻合。Zhou等[26]使用MSE模型成功模拟出KH2PO4-C2H5OH-H2O体系中磷酸二氢钾的结晶过程,为磷酸二氢钾的反溶剂结晶过程提供了基本的热力学参考。Foroozan等[27]使用e-NRTL模型拟合了烷烃、CO2水合物在甲醇和盐溶液中的溶解度数据,拟合结果与实验值具有非常高的一致性。
在模拟计算方面,对结晶过程模拟预测的软件目前也被越来越广泛的使用到结晶过程的研究中,比如OLI、Factsage、Aspen Plus、Materials Studio等。OLI是一款可用来计算多种混合电解质组分体系的相平衡过程的软件[33]。刘昶江等[34]采用OLI中的MSE模型进行了富钾正长岩-NaOH-H2O体系的相平衡模拟,并将结果成功运用到实验中。Factsage计算软件是由加拿大Thermfact/CRCT和德国GTT-Technologies联合研发的一款完全集成各大数据库的计算软件,可以计算多元混合体系中各约束条件下的相平衡过程,并自动输出相图或表格数据[35-37]。Aspen Plus是由美国能源部组织的,以麻省理工学院为主的多家高校和公司参与开发的一款大型过程模拟软件,自带庞大的数据库,广泛应用于化工各个领域中。Wang等[38]应用Aspen Plus软件中的Pitzer模型计算了NH4Cl体系固液相平衡和活度系数,与文献数据有高度的一致性。Materials Studio (MS)是一款由Accelrys公司开发的基于分子层面上的一款模拟计算软件,在化工、制药、航天等领域应用十分广泛,对分子动力学和热力学数据都具有良好的预测效果[39, 40]。吴剑铭等[41]用MS分子模拟探究了反式-1,4-聚异戊二烯不同晶型的生产条件。数据模拟和实验相结合是越来越受研究者关注的一种研究方式。热力学模拟计算能够通过有限的实验推导出更多的热力学数据,减少实验工作量,而且能够为实验结果的理论分析提供指导。
对于离子液体为溶剂的固液平衡体系,一般可以使用UNIQUAC模型、COSMO-RS模型等进行溶解度数据的关联和预测。Catarina等[42]使用了UNIQUAC模型预测了吡嗪-2-甲酰胺在离子液体中的固液平衡数据,关联度较高。此外,对于新兴的低共熔溶剂(DESs)[43],COSMO-RS模型也有很好的预测能力[44],能够为低共熔溶剂体系的发展和应用提供理论基础。
2 过饱和度和介稳区 2.1 过饱和度和介稳区的表示当溶液浓度超过溶解度时,该溶液称为过饱和溶液。过饱和度有多种表示方法,常用的有浓度差ΔC、过饱和度比S等。
| $ \Delta C=C-C^* $ | (1) |
| $ S = C / C^* $ | (2) |
式(1)~式(2)中:C为实际溶液浓度,C*为溶质在该条件下的饱和浓度(溶解度)。
过饱和度的产生是结晶的前提,只有当溶液处于过饱和状态才可以从溶液中结晶出晶体[45]。一般来讲,可以通过改变温度、蒸发溶剂、化学反应以及改变溶液组分等方式产生过饱和度[46]。过饱和溶液自发成核时的极限浓度就是该溶质的超溶解度,溶解度和超溶解度之间的区域就称为介稳区,如图 1所示[47]。

|
| 图 1 介稳区宽度示意图 Fig.1 Schematic diagram of the metastable zone width |
| |
介稳区是结晶过程的最佳操作区域,在介稳区内可以有效调节晶体的粒度分布、形态等方面。当溶液的过饱和度超过介稳区进入不稳定区域时,溶液就会爆发成核,快速产生大量的细小颗粒,不利于后续的过滤等操作。此时晶体成核方式主要为初级成核,由于初级成核过程的复杂性,其成核机理一直是结晶领域研究的难点。工业领域更关注易于控制的二次成核,二次成核过程可以更好地控制产品的粒度、晶型和手性等[48]。因此,介稳区的测定对结晶过程优化是非常重要的。
目前对介稳区宽度的测定方法大致分为2类,1种是检测晶体成核量的变化,例如浊度计法[49]和聚集光束反射测量仪(FBRM)[50]等;1种是检测溶液浓度的变化,如红外光谱仪[51]和电导率法[52]等。随着现代技术的发展,传统的目测[53]等方法由于其自身的精确度不高正在逐步被仪器测定方法替代。Liang等[54]使用电导率法测定了葡萄糖酸钙在水中的超溶解度曲线;Wang等[55]使用激光仪器在线测定了Na3VO4介稳区宽度。介稳区宽度容易受外界因素影响,导致介稳区宽度发生改变的外界因素有很多种,例如温度、搅拌速率、降温速度、溶剂的种类、杂质和稳定剂等等[56-60]。Zhang等[61]测定了磷酸脲溶液的介稳区,并且验证了搅拌速率会使得介稳区变窄,杂质的加入和冷却速率的提高则会使介稳区宽度增加。Sameer等[62]对姜黄素的结晶过程中使用稳定剂进行处理,结果发现稳定剂对介稳区和诱导时间的增加产生了一定作用。
传统测定方法有一些局限性,例如精度不高,晶核出现时间难以判定等,同时也仅仅是在宏观尺度下的测定。近些年来,越来越多的研究者开始将微流体技术和光学系统结合使用进行介稳区的研究[63]。微流体技术精度高、效率高,未来介稳区的主流测定方式将会越来越倾向于微流体技术的应用。
介稳区属于非平衡热力学的范畴,目前只有一些半经验半理论的模型可以进行关联。Nývlt模型是广泛认可的可以用来关联介稳区的数学模型[64],在一定程度上对介稳区有很好的预测效果,但是也有如无法解释温度如何对介稳区产生影响的缺点。Kubota[65]提出了一种新的介稳区模型,不过仍没有克服Nývlt模型的内在缺点,使用也并不广泛。此外,Sangwal[66]基于正规溶液理论提出了一种介稳区预测模型,但是无法说明降温速率和饱和温度对介稳区的影响。未来关于介稳区的预测模型方面的研究还有待深入。
3 相图及其应用 3.1 相图的种类相图能够表示相平衡系统与温度和压力等参数之间的关系,可以为结晶过程提供重要的热力学数据,如平衡时的相数、组成和含量等。根据相图可以分析盐类体系中各组分溶解或析出的时间先后以及组成含量的变化趋势,决定了溶剂的选择、晶体的收率以及过饱和生成方式等[67]。
相图有单组分相图,也有二元、三元及多元相图。有些体系,组分之间不会发生反应生成化合物。目前二元体系的研究已经十分深入,而实际应用中,往往都是多元组分,所以三元以及多元体系是现阶段研究的主流方向。曹大群等[68]采用等温溶解平衡法测定了CaCl2-SrCl2-BaCl2-H2O四元体系及其三元子体系的相平衡溶解度数据,并绘制出三元相图,确定三元相图体系中的不变点,单变量曲线和结晶区,分析了该体系的盐溶解能力大小。张国俊等[69]利用等温溶解平衡法测定了313.15 K时LiCl-MgCl2-H2O的溶解度并绘制了三元相图,为盐湖卤水镁锂分离提供理论指导。
3.2 相图的应用三元相图在手性物质的拆分过程中起着非常好的作用。通过三元相图的几何学原理和平衡析晶过程中的各组成的移动轨迹,可以迅速判断出最优拆分方案,得到最大含量的所需手性物质。Cascella等[70]根据三元相图内两相和三相域的溶液和固相性质,提供了蛋氨酸2种手性分子的分离策略,并用实验验证了相图对于分离手性物质的有效应用。
溶质和溶剂以及溶质之间经常会发生化合反应形成一种或多种不同的化合物,成为溶剂化物或者共晶。相图的应用可以方便我们快速准确的确定固溶区的位置。张亚琪等[71]等采用溶度积理论对溶解度曲线进行拟合,并计算得到热力学参数,结合黄芩素-烟酰胺-乙酸乙酯的三元相图,指出温度对于共晶形成影响,为该共晶的放大生产提供了理论基础。Zhang等[72]采用静态法测定了ZnSO4-CuSO4-H2O和ZnSO4-ZnCl2-H2O体系在323 K,0.1 MPa下的相平衡数据,通过三元相图研究了盐析作用并预测了固溶体的存在。王肖丽等[73]使用湿渣法与X射线衍射相结合的方法测定了四元体系NH4+-KH2PO4-CO(NH2)2-H2O的固液相平衡数据,绘制相应的三元子体系相图,找到相图中的固溶体结晶区,为共结晶作出理论指导。
为了研究介稳状态,研究者们也提出了介稳相图的概念。韦健等[74]在研究覆盆子酮结晶过程的油析现象时,通过测定覆盆子酮的溶解度和超溶解度数据绘制出介稳相图,明确了覆盆子酮结晶优化的新思路。相图也是结晶过程原料选择的重要依据。冯珊[75]采用等温蒸发法开展了2个四元体系Li+-Na+-KCl-H2O、KCl--CO32--SO42--H2O在温度为273 K下的介稳相平衡研究,从绘制出的介稳相图得到了几种盐类的盐析作用的强弱。
4 结晶过程分析技术 4.1 离线分析技术检测技术大致可以分为3种,分别是离线、在线和原位方法。离线法是通过手工采集样品,然后在实验室进行离线分析,一般都需要比较繁琐的预处理,才能保证实验的准确性。对于结晶体系中液相组分的分析,离线方法主要有重量法、色谱法和折射率法等。重量法是当溶液达到固液平衡时,通过蒸发溶剂得到纯溶质的质量来计算原溶液组分,一般可以用于稳定晶型或者转相较慢的介稳晶型的浓度测定[76]。色谱法的原理是基于不同物质在不同相态的选择性分配,以流动相对固定相中的混合物进行洗脱,混合物中不同的物质会以不同的速度沿固定相移动,最终达到分离的效果。色谱法可以分为气相色谱法、液相色谱法和超高效液相色谱法,针对不同物质的分析采用不同的色谱分析法[77-80]。折射率法的原理是不同溶液浓度与其折射率呈线性关系,以此可以得出溶液浓度[81, 82]。
4.2 在线和原位分析技术因为离线法耗时长,过程繁琐,且在离线处理过程中会对结果产生干扰,所以研究者们寻求更为快速有效的检测方法。目前在线分析技术已成为结晶领域重要的表征手段。量热法是根据热平衡原理发展出来的一种检测方法,它通过测量温度等数据和能量平衡结合起来,从而计算出结晶热、溶液浓度等热力学数据[83, 84]。超声波法的原理是超声波在通过不同浓度的溶液时,速度会随之发生改变,以此算出溶液浓度。Xu等[85]采用超声波在线测量阿司匹林结晶过程,验证了超声波在结晶过程测量中的高可行性和可靠性。
基于近些年光谱技术的迅速发展,原位测量在结晶过程中的应用越加广泛。利用红外光谱和拉曼散射光谱的分析方法易于操作,重复性高,是最常用的原位测量方法[86]。红外检测光谱是吸收光谱[87],衰减全反射-傅里叶变换红外光谱仪(ATR-FTIR)常用来原位检测溶液里液相组分,该仪器通过探头附近样品表面的红外反射信号来获得溶液信息,分析速度快、效率高,且不会对分析样品产生破坏性影响,但是其使用局限性在于检测的组分含量一般要大于0.1%,维护成本相对较高,并且需要依赖一定的分析模型。Yang等[88]采用在线红外光谱测定了吲哚美辛在不同混合溶剂的溶解度并进行了热力学模拟,分析了溶剂对溶解度的影响,为溶析结晶中溶剂的筛选给出了指导。拉曼光谱是基于散射原理确定溶液或固体组分的一种在线分析方法,拉曼光谱由于自身特殊性则多用于检测悬浮液中的固体浓度和晶型转变以及表征共晶的形成等[89, 90]。拉曼光谱检测可以分析较低浓度中的组分含量,但是因为检测的是物质化学键的信息,所以一般无法检测金属单质等[91]。Yang等[92]采用原位拉曼光谱研究了HNIW多晶型物的过饱和体系,成功测量了结晶过程中的成核动力学和饱和浓度数据。Du等[93]采用拉曼散射光谱监测了共晶的形成过程,实时监控共晶反应,为从分子水平了解其反应机理提供了潜在的工具。
除了对于溶液结晶过程的监测以外,对于结晶固体也需要一定的分析检测,例如晶体的粒度、形貌和晶型等方面[94-96]。在离线检测方面,晶体粒度分析主要采用粒度仪,可以直接得到晶体的粒度分布[97]。形貌结构一般使用光学显微镜、扫描电镜(SEM)和透射电镜(TEM)进行分析,2种电镜可以将晶体从表面到内部的形貌结构观察的较为详细,能清楚分析组成晶体的微观形貌、孔径以及晶格条纹等[98]。此外,电子反向散射衍射(EBSD)为电镜分析做了很好的优化,在微观组织结构及微织构表征中被广泛应用[99, 100]。晶型分析的最主要的方法则是X射线衍射(XRD),主要可以通过XRD谱图与标准谱图的不同来区分不同的晶型[101, 102]。近年来随着技术的发展,在线固体检测技术也越来越成熟。聚集光束反射测量仪(FBRM)是在线测定晶体弦长的一种常见的过程分析技术工具,可以用于监测结晶过程中的晶体的弦长分布(CLD)特性[103, 104]。在线颗粒影像测量技术也是近些年被广泛使用的一种在线晶体检测技术工具,可以得到结晶过程的晶体形貌和颗粒照片[105, 106]。
采用过程分析技术对结晶过程进行表征和实时监控能够帮助我们更深层次理解结晶机理和进行产品质量控制,其便捷性和有效性已经得到普遍认可。目前过程分析技术操作壁垒仍然存在,比如对成核前分子团簇的直接表征或者对晶体生长界面层的表征等仍然存在困难。未来更为先进的检测分析技术的开发对于结晶机理的认识和结晶过程的精准调控有非常重要的作用。
5 结语溶解度、相图等基本热力学性质对结晶过程的优化和结晶路线的设计等方面有重要的指导意义。分析方法和软件的使用是深入研究结晶过程的手段,未来会越来越多地采用原位测量方式获取结晶过程中的实验数据,利用更加准确的活度系数方程进行更加全面的模拟计算。无论是实验分析还是模拟计算,对于不同的体系采用合适的方法是非常关键的,因此热力学也在朝向普适化和精准化2个方向发展。结晶热力学的研究还有非常多待探索的空间,例如如何基于热力学原理对晶型进行准确调控,如何通过微观界面的热力学研究来分析成核和生长机理,如何将结晶过程数据的监测和新兴技术进行耦合等。表征分析技术以及模拟计算技术的发展一定会加速结晶领域的深入认识和全面发展。
| [1] |
NANEV C N. Advancements (and challenges) in the study of protein crystal nucleation and growth; thermodynamic and kinetic explanations and comparison with small-molecule crystallization[J]. Progress in Crystal Growth and Characterization of Materials, 2020. DOI:10.1016/j.pcrysgrow.2020.100484 |
| [2] |
黄炎, 孙海龙, 孟子超, 等. 溶析结晶在医药领域的研究进展[J]. 化工进展, 2019, 38(5): 2380-2388. HUANG Yan, SUN Hailong, MENG Zichao, et al. Progress in antisolvent crystallization in pharmaceutical field[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2019, 38(5): 2380-2388. (in Chinese) |
| [3] |
LINDENMEYER P H. Surface area and secondary nucleation theory[J]. Nature, 1977, 269(5627): 396-397. DOI:10.1038/269396a0 |
| [4] |
NAGALINGAM S, VASUDEVAN S, RAMASAMY P, et al. Studies on two-dimensional nucleation[J]. Journal of Crystal Growth, 1982, 57(2): 387-390. DOI:10.1016/0022-0248(82)90495-X |
| [5] |
TAI C, WU J, ROUSSEAU R W. Interfacial supersaturation, secondary nucleation, and crystal growth[J]. Journal of Crystal Growth, 1992, 116(3/4): 294-306. |
| [6] |
CADORET R, HOTTIER F. Mechanism of Si polycrystalline growth on a Si3N4 substrate from SiH4/H2 at reduced pressures[J]. Journal of Crystal Growth, 1983, 64(3): 583-592. DOI:10.1016/0022-0248(83)90345-7 |
| [7] |
胡程耀, 黄培. 固体溶解度测定方法的近期研究进展[J]. 药物分析杂志, 2010, 30(4): 761-766. HU Chengyao, HUANG Pei. Recent research progress in solid solubility determination methods[J]. Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis, 2010, 30(4): 761-766. (in Chinese) |
| [8] |
张婵, 程文婷, 成怀刚, 等. AlCl3 ·6H2O在FeCl3-CaCl2-HCl-H2O体系中溶解度的模拟和测定[J]. 无机盐工业, 2019, 51(5): 61-65. ZHANG Chan, CHENG Wenting, CHENG Huaigang, et al. Simulation and determination of AlCl3 ·6H2O solubility in FeCl3-CaCl2-HCl-H2O system[J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2019, 51(5): 61-65. (in Chinese) |
| [9] |
LI D, MENG L, DENG T, et al. Experimental and thermodynamic modeling study of solid-liquid equilibrium in ternary systems NaBr-SrBr2-H2O and KBr-SrBr2-H2O at 288.15 K and 0.1 MPa[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2018, 252: 362-367. DOI:10.1016/j.molliq.2018.01.020 |
| [10] |
王海蓉, 张春桃, 梁文懂. 赤藓糖醇在水中的结晶热力学及结晶过程研究[J]. 化学工业与工程, 2018, 35(3): 50-54. WANG Hairong, ZHANG Chuntao, LIANG Wendong. Crystallization thermodynamics and its crystallization process of meso-erythritol in water[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering, 2018, 35(3): 50-54. (in Chinese) |
| [11] |
张妍. 七水硫酸亚铁综合利用绿色新工艺及相关基础研究[D]. 北京: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院过程工程研究所), 2017 ZHANG Yan. New green process for comprehensive utilization of ferrous sulfate and relevant fundamental investigation[D]. Beijing: Institute of Process Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2017 (in Chinese) |
| [12] |
LONG B, XIA Y, DENG Z, et al. Understanding the enhanced solubility of 1, 3-benzenedicarboxylic acid in polar binary solvents of (acetone+water) at various temperatures[J]. The Journal of Chemical Thermodynamics, 2017, 105: 105-111. DOI:10.1016/j.jct.2016.10.011 |
| [13] |
CRESTANI C E, BERNARDO A, COSTA C B B. Fructose solubility in mixed (ethanol+water) solvent: Experimental data and comparison among different thermodynamic models[J]. Journal of Chemical and Engineering Data: the ACS Journal for Data, 2013, 58(11): 3039-3045. DOI:10.1021/je400471m |
| [14] |
梁玺, 赵改菊, 路春美, 等. 葡萄糖酸钙结晶的热力学特性[J]. 化学工程, 2021, 49(3): 22-27. LIANG Xi, ZHAO Gaiju, LU Chunmei, et al. Thermodynamic properties of calcium gluconate crystallization[J]. Chemical Engineering (China), 2021, 49(3): 22-27. (in Chinese) |
| [15] |
刘珏欣, 郑承刚, 叶世超. 磷酸二氢钾结晶热力学数据的测定及应用研究[J]. 无机盐工业, 2021, 53(1): 62-64. LIU Juexin, ZHENG Chenggang, YE Shichao. Determination and application of thermodynamic data of potassium dihydrogen phosphate crystal[J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2021, 53(1): 62-64. (in Chinese) |
| [16] |
房彬彬, 侯宝红, 黄欣, 等. 二苯甲酮结晶热力学性质及其模型研究[J]. 化学工业与工程, 2019, 36(6): 1-8. FANG Binbin, HOU Baohong, HUANG Xin, et al. Research on thermodynamic properties and model of benzophenone[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering, 2019, 36(6): 1-8. (in Chinese) |
| [17] |
JOLLIFFE H G, DIAB S, GEROGIORGIS D I. Nonlinear optimization via explicit NRTL model solubility prediction for antisolvent mixture selection in artemisinin crystallization[J]. Organic Process Research & Development, 2018, 22(1): 40-53. |
| [18] |
LI C, JI X, LI J, et al. Measurement and correlation of the solubility of kojic acid in pure and binary solvents[J]. The Journal of Chemical Thermodynamics, 2022. DOI:10.1016/j.jct.2021.106712 |
| [19] |
彭小奇, 宋国辉, 宋彦坡, 等. NaOH-NaAl(OH)4-Na2CO3-H2O体系活度因子的计算模型[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2009, 19(7): 1332-1337. PENG Xiaoqi, SONG Guohui, SONG Yanpo, et al. Calculation model of activity coefficient for NaOH-NaAl(OH)4-Na2CO3-H2O system[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2009, 19(7): 1332-1337. (in Chinese) |
| [20] |
GAO W, LI Z. Solubility and K-Sp of Mg4Al2(OH)14 center dot 3H2O at the various ionic strengths[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2012, 117: 36-46. |
| [21] |
PABLO L, TURNER D R, ACHTERBERG E P, et al. Solid-liquid equilibria in aqueous solutions of tris, tris-NaCI, tris-TrisHCl, and tris-(TrisH)(2)SO4 at temperatures from 5 to 45 ℃[J]. Journal of Chemical and Engineering Data, 2021, 66(1): 437-455. DOI:10.1021/acs.jced.0c00744 |
| [22] |
KHORSANDI M, SHEKAARI H, MOKHTARPOUR M, et al. Cytotoxicity of some choline-based deep eutectic solvents and their effect on solubility of coumarin drug[J]. European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 2021. DOI:10.1016/j.ejps.2021.106022 |
| [23] |
张妍, ZENG Yan, 李志宝, 等. 电解质溶液化学模型理论最新进展及应用举例[J]. 沈阳化工大学学报, 2017, 31(1): 1-8. ZHANG Yan, ZENG Yan, LI Zhibao, et al. Speciation-based chemical modeling of electrolyte solution and its application[J]. Journal of Shenyang University of Chemical Technology, 2017, 31(1): 1-8. (in Chinese) |
| [24] |
WANG P, ANDERKO A, YOUNG R D. A speciation-based model for mixed-solvent electrolyte systems[J]. Fluid Phase Equilibria, 2002, 203(1/2): 141-176. |
| [25] |
ZHANG X, ZENG Y, LI Z. Accelerated phase transition and synthesis of magnesite from hydromagnesite in aqueous mono-ethylene glycol solution[J]. Journal of Crystal Growth, 2021. DOI:10.1016/j.jcrysgro.2021.126105 |
| [26] |
ZHOU X, ZHENG W, XU D, et al. Solubility measurement and thermodynamics modelling for potassium dihydrogen phosphate in a water-ethanol system from 293.2 to 323.2 K[J]. Fluid Phase Equilibria, 2020. DOI:10.1016/j.fluid.2020.112533 |
| [27] |
KESHAVARZI F, JAVANMARDI J, NASRIFAR K, et al. Determination of clathrate hydrates dissociation conditions in aqueous solutions of methanol and salt using the e-NRTL based model[J]. Fluid Phase Equilibria, 2021. DOI:10.1016/j.fluid.2021.113121 |
| [28] |
ZHANG H, CHENG Z, TANG X, et al. Determination and correlation of solubility of potassium dihydrogen phosphate in acetonitrile-water solvent[J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2022, 54(1): 83-85. |
| [29] |
SALIMI A, ROOSTA A. Experimental solubility and thermodynamic aspects of methylene blue in different solvents[J]. Thermochimica Acta, 2019, 675: 134-139. DOI:10.1016/j.tca.2019.03.024 |
| [30] |
CHEN X, XU J, GU J, et al. Measurement and correlation of the solubility of gestodene in 11 pure and binary mixed solvent systems at temperatures from 283.15 to 323.15 K[J]. Journal of Chemical and Engineering Data, 2021, 66(10): 3776-3787. DOI:10.1021/acs.jced.1c00408 |
| [31] |
NARJES M S, MOHAMMAD B J, FLEMING M, et al. Solubility of lamotrigine in acetonitrile+water mixtures at various temperatures[J]. Physics and Chemistry of Liquids, 2020, 58(6): 769-781. DOI:10.1080/00319104.2019.1636380 |
| [32] |
SEYF J Y, SHOJAEIAN A. Vapor-liquid (azeotropic systems) and liquid-liquid equilibrium calculations using UNIFAC and NRTL-SAC activity coefficient models[J]. Fluid Phase Equilibria, 2019, 494: 33-44. DOI:10.1016/j.fluid.2019.04.029 |
| [33] |
宋静, 齐涛, 曲景奎. OLI相平衡模拟软件及其在铬盐清洁新工艺中的应用[C]//2012年全国冶金物理化学学术会议专辑(上册). 昆明, 2012
|
| [34] |
刘昶江, 马鸿文, 张盼. 富钾正长岩水热分解生成沸石反应热力学[J]. 物理化学学报, 2018, 34(2): 168-176. LIU Changjiang, MA Hongwen, ZHANG Pan. Thermodynamics of the hydrothermal decomposition reaction of potassic syenite with zeolite formation[J]. Acta Physico-Chimica Sinica, 2018, 34(2): 168-176. (in Chinese) |
| [35] |
尚志标, 黄小凤, 马丽萍, 等. 复合晶核剂对黄磷炉渣微晶玻璃析晶的影响[J]. 人工晶体学报, 2017, 46(8): 1643-1648, 1652. SHANG Zhibiao, HUANG Xiaofeng, MA Liping, et al. Effect of composite nucleation agents on crystallization of glass-ceramics produced by yellow phosphorus furnace slag[J]. Journal of Synthetic Crystals, 2017, 46(8): 1643-1648, 1652. (in Chinese) |
| [36] |
SCHWITALLA D H, BRONSCH A M, KLINGER M, et al. Analysis of solid phase formation and its impact on slag rheology[J]. Fuel, 2017, 203: 932-941. DOI:10.1016/j.fuel.2017.04.092 |
| [37] |
DENG J, CHENG L, ZHENG G, et al. Thermodynamic study on co-deposition of ZrB2-SiC from ZrCl4-BCl3-CH3SiCl3-H2-Ar system[J]. Thin Solid Films, 2012, 520(23): 7030-7034. DOI:10.1016/j.tsf.2012.07.105 |
| [38] |
WANG D, LI Z. Kinetic analysis for crystal growth rate of NH4Cl in the NaCl-MgCl2-H2O system with a thermodynamic approach[J]. AIChE Journal, 2012, 58: 914-924. DOI:10.1002/aic.12604 |
| [39] |
CONSTANCE E N, MOHAMMED M, MOJIBOLA A, et al. Effect of additives on the crystal morphology of amino acids: A theoretical and experimental study[J]. Journal f Physical Chemistry, 2016, 120(27): 14749-14757. |
| [40] |
高毅颖, 张懿, 王静康, 等. 不同类型媒晶剂对硫酸铵晶体形态学指标的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2011, 62(12): 3575-3579. GAO Yiying, ZHANG Yi, WANG Jingkang, et al. Effect of crystallization additives on crystal morphology of ammonium sulfate[J]. CIESC Journal, 2011, 62(12): 3575-3579. (in Chinese) |
| [41] |
吴剑铭, 王小蕾, 汤琦, 等. 反式聚异戊二烯结晶性能与分子模拟的研究进展[J]. 高分子材料科学与工程, 2019, 35(7): 167-174. WU Jianming, WANG Xiaolei, TANG Qi, et al. Progress in crystallization properties and molecular simulations of trans-1, 4-polyisoprene[J]. Polymer Materials Science & Engineering, 2019, 35(7): 167-174. (in Chinese) |
| [42] |
LOURENÇO C, MELO C I, BOGEL-ŁUKASIK R, et al. Solubility advantage of pyrazine-2-carboxamide: Application of alternative solvents on the way to the future pharmaceutical development[J]. Journal of Chemical & Engineering Data, 2012, 57: 1525-1533. |
| [43] |
PETITPREZ J, LEGRAND F X, TAMS C, et al. Huge solubility increase of poorly water-soluble pharmaceuticals by sulfobutylether-β-cyclodextrin complexation in a low-melting mixture[J]. Environmental Chemistry Letters, 2022, 20(3): 1561-1568. DOI:10.1007/s10311-022-01415-y |
| [44] |
KAMGAR A, MOHSENPOUR S, ESMAEILZADEH F. Solubility prediction of CO2, CH4, H2, CO and N2 in choline chloride/urea as a eutectic solvent using NRTL and COSMO-RS models[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2017, 247: 70-74. DOI:10.1016/j.molliq.2017.09.101 |
| [45] |
LINNIKOV O D. Mechanism of precipitate formation during spontaneous crystallization from supersaturated aqueous solutions[J]. Russian Chemical Reviews, 2014, 83(4): 343-364. DOI:10.1070/RC2014v083n04ABEH004399 |
| [46] |
MULLIN J W. Crystallization[M]. The United Kingdom: Reed educational and professional publishing ltd, 2001.
|
| [47] |
MERSMANN A, LÖFFELMANN M. Crystallization and precipitation: The optimal supersaturation[J]. Chemie Ingenieur Technik, 1999, 71: 1240-1244. DOI:10.1002/cite.330711103 |
| [48] |
BECKMANN W. Seeding the desired polymorph: Background, possibilities, limitations, and case studies[J]. Organic Process Research & Development, 2000, 4(5): 372-383. |
| [49] |
WANG H, DU B, WANG M. Study of the solubility, supersolubility and metastable zone width of Li2CO3in the LiCl-NaCl-KCl-Na2SO4 System from 293.15 to 353.15K[J]. Journal of Chemical & Engineering Data, 2018, 63(5): 1429-1434. |
| [50] |
王盼盼, 余培斌, 吴麒峰, 等. 冷冻共晶法结晶谷氨酸钠介稳区测定[J]. 化学工程, 2017, 45(10): 33-36, 40. WANG Panpan, YU Peibin, WU Qifeng, et al. Determination of freezing eutectic crystalization metastable zone of monosodium glutamate[J]. Chemical Engineering (China), 2017, 45(10): 33-36, 40. (in Chinese) |
| [51] |
O'GRADY D, BARRETT M, CASEY E, et al. The effect of mixing on the metastable zone width and nucleation kinetics in the anti-solvent crystallization of benzoic acid[J]. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 2007, 85(7): 945-952. DOI:10.1205/cherd06207 |
| [52] |
LIU X, ZHANG Z, ZHANG L, et al. Thermodynamic study on evaporation crystallization of high saline wastewater from lead-acid batteries[J]. Journal of Crystal Growth, 2021. DOI:10.1016/j.jcrysgro.2021.126166 |
| [53] |
SAHIN O, DOLAS H, DEMIR H. Determination of nucleation kinetics of potassium tetraborate tetrahydrate[J]. Crystal Research and Technology, 2007, 42(8): 766-772. DOI:10.1002/crat.200710904 |
| [54] |
LIANG X, ZHAO G, LU C, et al. Thermodynamic properties of calcium gluconate crystallization[J]. Chemical Engineering (China), 2021, 49(3): 22-27. |
| [55] |
WANG S, FENG M, DU H, et al. Determination of metastable zone width, induction time and primary nucleation kinetics for cooling crystallization of sodium orthovanadate from NaOH solution[J]. Journal of Crystal Growth, 2020. DOI:10.1016/j.jcrysgro.2020.125721 |
| [56] |
沈金玉, 梅文斌, 曹竹安. 丙烯酰胺的结晶热力学[J]. 精细化工, 2002, 19(4): 244-247. SHEN Jinyu, MEI Wenbin, CAO Zhuan. Crystallization thermodynamics of acrylamide[J]. Fine Chemicals, 2002, 19(4): 244-247. (in Chinese) |
| [57] |
MILOSLAV K, JAROSLAV N. Effect of impurities on the width of the metastable region of potassium sulfate[J]. Collection of Czechoslovak Chemical Communications, 1993, 58(9): 1997-2002. DOI:10.1135/cccc19931997 |
| [58] |
姜东波, 曾英, 于旭东. 三元体系NaCl+NH4Cl+H2O 323.15K介稳相关系研究[J]. 应用化工, 2013, 42(4): 599-601. JIANG Dongbo, ZENG Ying, YU Xudong. Metastable phase equilibrium in the ternary system NaCl+NH4Cl+H2O at 323.15 K[J]. Applied Chemical Industry, 2013, 42(4): 599-601. (in Chinese) |
| [59] |
何兴学, 孙勤, 杨阿三, 等. 醋酸钠介稳区的测定[J]. 化学工程, 2012, 40(7): 43-45. HE Xingxue, SUN Qin, YANG Asan, et al. Determination of metastable region for sodium acetate[J]. Chemical Engineering (China), 2012, 40(7): 43-45. (in Chinese) |
| [60] |
CHEN Q, WANG J, BAO Y. Determination of the crystallization thermodynamics and kinetics of L[J]. Fluid Phase Equilibria, 2012, 313: 182-189. DOI:10.1016/j.fluid.2011.09.028 |
| [61] |
ZHANG L, WANG B, TANG J, et al. Determination of the metastable zone and induction period of urea phosphate solution[J]. International Journal of Chemical Reactor Engineering, 2019. DOI:10.1515/ijcre-2018-0174 |
| [62] |
DALVI S V, YADAV M D. Effect of ultrasound and stabilizers on nucleation kinetics of curcumin during liquid antisolvent precipitation[J]. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 2015, 24: 114-122. DOI:10.1016/j.ultsonch.2014.11.016 |
| [63] |
LIU Y, WANG Y, LIU Y, et al. Solubility of L-histidine in different aqueous binary solvent mixtures from 283.15 K to 318.15 K with experimental measurement and thermodynamic modelling[J]. The Journal of Chemical Thermodynamics, 2017, 105: 1-14. |
| [64] |
XU S, WANG J, ZHANG K, et al. Nucleation behavior of eszopiclone-butyl acetate solutions from metastable zone widths[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2016, 155: 248-257. |
| [65] |
Kubota N. A new interpretation of metastable zone widths measured for unseeded solutions[J]. Journal of Crystal Growth, 2008, 310(3): 629-634. |
| [66] |
SANGWAL K. A novel self-consistent Nvlt-like equation for metastable zone width determined by the polythermal method[J]. Crystal Research & Technology, 2010, 44(4): 231-247. |
| [67] |
LI X, YIN Q, ZHANG M, et al. Process design for antisolvent crystallization of erythromycin ethylsuccinate in oiling-out system[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2016, 55(27): 7484-7492. |
| [68] |
曹大群, 金艳, 陈杭, 等. 338.15 K时四元体系CaCl2-SrCl2-BaCl2-H2O相平衡测定及溶解度计算[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(10): 5028-5039. CAO Daqun, JIN Yan, CHEN Hang, et al. Phase equilibria determination and solubility calculation of the quaternary system CaCl2-SrCl2-BaCl2-H2O at 338.15 K[J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(10): 5028-5039. (in Chinese) |
| [69] |
张国俊, 保英莲, 刘鲤君, 等. LiCl-MgCl2-H2O三元水盐体系在313.15K相平衡研究[J]. 广州化工, 2021, 49(14): 52-54. ZHANG Guojun, BAO Yinglian, LIU Lijun, et al. Phase equilibrium of LiCl-MgCl2-H2O ternary water salt system at 313.15 K[J]. Guangzhou Chemical Industry, 2021, 49(14): 52-54. (in Chinese) |
| [70] |
CASCELLA F, SEIDEL-MORGENSTERN A, LORENZ H. Exploiting ternary solubility phase diagrams for resolution of enantiomers: An instructive example[J]. Chemical Engineering & Technology, 2020, 43(2): 329-336. |
| [71] |
张亚琪, 黄燕婷, 高缘, 等. 黄芩素-烟酰胺共晶结晶过程的热力学研究[J]. 中国药科大学学报, 2015, 46(5): 568-574. ZHANG Yaqi, HUANG Yanting, GAO Yuan, et al. Thermodynamics of baicalein-nicotinamide co-crystallization process[J]. Journal of China Pharmaceutical University, 2015, 46(5): 568-574. (in Chinese) |
| [72] |
ZHANG X, YAN S, ZHOU S, et al. Solid liquid phase equilibria in the ternary systems ZnSO4-CuSO4-H2O and ZnSO4-ZnCl2-H2O at 323 K and 0.1 MPa[J]. Journal of Chemical and Engineering Data, 2020, 65(6): 2957-2963. |
| [73] |
王肖丽, 朱静, 吴强, 等. NH4+, K+//H2PO4--CO(NH2)2-H2O四元体系298.15 K相平衡研究[J]. 化学工程, 2021, 49(8): 39-44. WANG Xiaoli, ZHU Jing, WU Qiang, et al. NH4+, K+//H2PO4--CO(NH2)2-H2O quaternary system 298.15 K phase equilibrium study[J]. chemical engineering, 2021, 49(8): 39-44. (in Chinese) |
| [74] |
韦健, 朱亮, 沙作良, 等. 覆盆子酮油析结晶过程研究[J]. 化学工业与工程, 2022, 39(1): 66-74. WEI Jian, ZHU Liang, SHA Zuoliang, et al. Investigation on the oiling out crystallization of raspberry ketone[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering, 2022, 39(1): 66-74. (in Chinese) |
| [75] |
冯珊. 扎布耶盐湖含锂五元体系273 K介稳相图研究及老卤蒸发实验[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2015 FENG Shan. Metastable phase equilibria for quinary system contained with lithium and isothermal evaporation of the zabuye old brine[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2015 (in Chinese) |
| [76] |
MO Y, DANG L, WEI H. Solubility of α-form and β-form of L-glutamic acid in different aqueous solvent mixtures[J]. Fluid Phase Equilibria, 2011, 300(1/2): 105-109. |
| [77] |
VON MUHLEN C, LANCAS F M. Unified chromatography[J]. Quimica Nova, 2004, 27(5): 747-753. |
| [78] |
VEVELSTAD S J, GRIMSTVEDT A, ELNAN J, et al. Oxidative degradation of 2-ethanolamine: The effect of oxygen concentration and temperature on product formation[J]. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control, 2013, 18: 88-100. |
| [79] |
VAN TRICHT E, DE RAADT P, VERWILLIGEN A, et al. Fast, selective and quantitative protein profiling of adenovirus-vector based vaccines by ultra-performance liquid chromatography[J]. Journal of Chromatography A, 2018, 1581/1582: 25-32. |
| [80] |
REDEUIL K, VULCANO J, PRENCIPE F P, et al. First quantification of nicotinamide riboside with B3 vitamers and coenzymes secreted in human milk by liquid chromatography-tandem-mass spectrometry[J]. Journal of Chromatography B, Analytical Technologies in the Biomedical and Life Sciences, 2019, 1110/1111: 74-80. |
| [81] |
雷红, 李淑妮, 翟全国, 等. 298.15和308.15 K时1, 2-丙二醇+MCl(M=Na, K, Rb, Cs)+H2O三元体系的溶解度、密度和折光率[J]. 物理化学学报, 2012, 28(7): 1599-1607. LEI Hong, LI Shuni, ZHAI Quanguo, et al. Solubility, density and refractive index for the ternary systems of 1, 2-propanediol, MCl (M=Na, K, Rb, Cs) and H2O at 298.15 and 308.15 K[J]. Acta Physico-Chimica Sinica, 2012, 28(7): 1599-1607. (in Chinese) |
| [82] |
KRISHAN L. Densities, viscosities, and refractive indices of binary liquid mixtures of hexane, decane, hexadecane, and squalane with benzene at 298.15 K[J]. Journal of Chemical and Engineering Data: the ACS Journal for Data, 2000, 45(5): 961-964. |
| [83] |
MONNIER O, FEVOTTE G, HOFF C, et al. Model identification of batch cooling crystallizations through calorimetry and image analysis[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 1997, 52(7): 1125-1139. |
| [84] |
RAJEEV M, HEIKE L, MYERSON A S. Solubility measurement using differential scanning calorimetry[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2002, 41(19): 4854-4862. |
| [85] |
XU S, LI X. Simulation and on-line real-time measurement of aspirin crystalline particle size distribution based on ultrasound[J]. Advances in Intelligent Systems Research, 2017, 132: 57-63. |
| [86] |
DU Y, FANG H, ZHANG Q, et al. Spectroscopic investigation on cocrystal formation between adenine and fumaric acid based on infrared and Raman techniques[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 2016, 153: 580-585. |
| [87] |
张冬燕, 王戎瑞. 高功率中红外激光器的进展[J]. 激光与红外, 2011, 41(5): 487-491. ZHANG Dongyan, WANG Rongrui. Progress on mid-infrared lasers[J]. Laser & Infrared, 2011, 41(5): 487-491. (in Chinese) |
| [88] |
YANG L, ZHANG Y, CHENG J, et al. Solubility and thermodynamics of polymorphic indomethacin in binary solvent mixtures[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2019. DOI:10.1016/j.molliq.2019.111717 |
| [89] |
HANSEN S B, BERG R W. Raman spectroscopic studies of methane gas hydrates[J]. Applied Spectroscopy Reviews, 2009, 44(2): 168-179. |
| [90] |
方虹霞, 张琪, 张慧丽, 等. 腺嘌呤与富马酸共晶体的太赫兹光谱分析[J]. 物理化学学报, 2015, 31(2): 221-226. FANG Hongxia, ZHANG Qi, ZHANG Huili, et al. Terahertz spectroscopic analysis of adenine and fumaric acid cocrystals[J]. Acta Physico-Chimica Sinica, 2015, 31(2): 221-226. (in Chinese) |
| [91] |
RAVEENDRAN S, ALAM M M, KHAN M I K, et al. In situ formation, structural, mechanical and in vitro analysis of ZrO2/ZnFe2O4 composite with assorted composition ratios[J]. Materials Science & Engineering C, Materials for Biological Applications, 2020. DOI:10.1016/j.msec.2019.110504 |
| [92] |
YANG H, KIM J H, KIM K J. Study on the crystallization rates of beta- and epsilon-form HNIW in in-situ raman spectroscopy and FBRM[J]. Propellants Explosives Pyrotechnics, 2020, 45(3): 422-430. |
| [93] |
DU Y, ZHANG H, XUE J, et al. Raman and terahertz spectroscopical investigation of cocrystal formation process of piracetam and 3-hydroxybenzoic acid[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 2015, 139: 488-494. |
| [94] |
UWAYA G E, FAYEMI O E, SHERIF E S M, et al. Synthesis, electrochemical studies, and antimicrobial properties of Fe3O4 nanoparticles from Callistemon viminalis plant extracts[J]. Materials (Basel, Switzerland), 2020. DOI:10.3390/ma13214894 |
| [95] |
VARUN S, INDRAJIT K, GOUTAM B, et al. Synthesis, spectroscopic characterization, crystal structure, theoretical (DFT) studies and molecular docking analysis of biologically potent isopropyl 5-chloro-2-hydroxy-3-oxo-2, 3-dihydrobenzofuran-2-carboxylate[J]. Molecular Crystals and Liquid Crystals, 2022, 738(1): 106-127. |
| [96] |
CHEN G, LIU R, SONG C, et al. Preparation of hemihydrate gypsum with controllable morphology in glycerol-NaCl-water solutions with maleic acid[J]. Journal of Crystal Growth, 2021. DOI:10.1016/j.jcrysgro.2021.126360 |
| [97] |
QI M, YI T, MO Q, et al. Preparation of wheat straw nanocellulose by acid hydrolysis assisted high pressure homogenization[J]. Transaction of China Pulp and Paper, 2020, 35(3): 1-8. |
| [98] |
ZHIGALINA O M, KHMELENIN D N, IVANOV I M, et al. Structure of the Fe-Co nanowires obtained by template synthesis[J]. Crystallography Reports, 2021, 66(6): 1109-1116. |
| [99] |
TAN G, LI H, WANG Y, et al. Effect of Zener-Hollomon parameter on microstructure evolution of a HEXed PM nickel-based superalloy[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2021. DOI:10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.159889 |
| [100] |
JESENOVEC J, VARLEY J, KARCHER S E, et al. Electronic and optical properties of Zn-doped β-Ga2O3 Czochralski single crystals[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2021. DOI:10.1063/5.0050468 |
| [101] |
VATS R, AHLAWAT R. Structural and optical investigations of Gd2O3: Dy3+ Nanophosphor[J]. Advances in Basic Sciences (ICABS), 2019. DOI:10.1063/1.5122526 |
| [102] |
PAN Q, ZHANG H, GUO X, et al. Effects of different coatings on the crystal transformation of beta-HNIW[J]. Journal of Crystal Growth, 2021. DOI:10.1016/j.jcrysgro.2021.1261752 |
| [103] |
HEFFERNAN C, SOTO R, HODNETT B K, et al. Growth kinetics of curcumin form I[J]. Crystengcomm, 2020, 22(20): 3505-3518. |
| [104] |
FUNG P, MAH H, GOLDBERG A F G, et al. PAT-facilitated pharmaceutical crystallization development through mechanistic understanding[J]. Crystal Growth & Design, 2020, 20(12): 7882-7900. |
| [105] |
LUO Z, CUI Y, DONG W, et al. Morphological diversity of nitroguanidine crystals with enhanced mechanical performance and thermodynamic stability[J]. Journal of Crystal Growth, 2017, 480: 132-140. |
| [106] |
KUTLUAY S, ŞAHIN Ö, CEYHAN A A, et al. Design and optimization of production parameters for boric acid crystals with the crystallization process in an MSMPR crystallizer using FBRM® and PVM® technologies[J]. Journal of Crystal Growth, 2017, 467: 172-180. |
 2023, Vol. 40
2023, Vol. 40