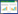异己烷包括2-甲基戊烷、3-甲基戊烷、2, 2-二甲基丁烷和2, 3-二甲基丁烷。异己烷是一种非极性溶剂,不溶于水,溶于乙醇、乙醚,还能溶解其他烃类及卤代烃,广泛应用于气雾、涂料、电子行业,主要用做无毒喷雾剂、溶剂、清洗剂等产品。甲基亚膦酸酯是合成非选择性广谱触杀性除草剂草铵膦的中间体。它是由甲基二氯磷与乙醇等低碳醇在缚酸剂存在下合成的。异己烷作为生产过程中溶剂[1],这就带来了异己烷和低碳醇的分离问题,需要知道异己烷和低碳醇的汽液平衡数据。
已经测定的异己烷与低碳醇的汽液平衡数据包括:2-甲基戊烷+乙醇[2],2-甲基戊烷+2-丙醇[3];3-甲基戊烷+乙醇[4],3-甲基戊烷+2-丙醇[5]。2, 2-二甲基丁烷和低碳醇的二元体系的汽液平衡数据还没有文献报道。为此,本研究测定了常压下2, 2-二甲基丁烷-乙醇和2, 2-二甲基丁烷-正丙醇二元体系的汽液平衡数据;并采用NRTL方程对实验数据进行了关联和估算。
1 实验部分 1.1 实验装置实验所用的汽液平衡釜是自行设计的汽液双循环装置,如图 1所示。

|
| 图 1 汽液平衡装置示意图 Figure 1 The apparatus for measuring the VLE data |
| |
该汽液平衡釜的主要优点包括:釜的主体部分有真空夹套保温层;汽相和液相形成独立的循环系统,不会形成返混,实验结果精确;透明的玻璃材质使得釜内的汽化现象清晰可见;样品用量少,达到平衡速度快,实验时间短。平衡釜的加热搅拌装置为恒温磁力搅拌器(巩义市英峪高科仪器厂,型号为SZCL-4)。平衡温度由已校正的精度为1/10的Pt-100电阻温度计(沈阳市中色测温仪表材料研究所有限公司)测量。
1.2 试剂无水乙醇和正丙醇,优级纯,天津市光复科技发展有限公司;蒸馏水,天津市南开区永源蒸馏水制造中心;2, 2-二甲基丁烷,色谱标准物,天津市津科精细化工研究所;2, 2-二甲基丁烷,质量分数99%,Alfa Aesar。
1.3 分析方法乙醇+水二元体系汽液平衡的汽相和液相的组成采用海能A650全自动折光仪(济南海能仪器有限公司)分析。
2, 2-二甲基丁烷+乙醇(正丙醇)二元体系汽液平衡的汽相和液相的组成采用Agilent 6820气相色谱仪分析,色谱柱为毛细管柱VF-5 ms(30 m,0.25 mm,0.25 μm),氢焰(FID)检测器,其他色谱条件见表 1,采用校正后的面积归一法进行定量。
| 2, 2-二甲基丁烷+乙醇 | 2, 2-二甲基丁烷+正丙醇 | |
| 进样量/μm | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| 柱前压/MPa | 0.095 | 0.1 |
| 分流模式 | 分流(分流比为200:1) | 分流(分流比为200:1) |
| 汽化室温度/℃ | 200 | 200 |
| 柱箱温度/℃ | 70 | 50 |
| 检测器温度/℃ | 200 | 200 |
| 载气 | 高纯氮 | 高纯氮 |
首先,在相应的气相色谱条件下分析不同摩尔分数的2, 2-二甲基丁烷+乙醇和2, 2-二甲基丁烷+正丙醇溶液,确定气相色谱的峰面积百分比与摩尔分数之间的关系,得到2种溶液的校正因子。
向汽液平衡釜内加入待测的二元组分混合物料约20 mL,打开冷冻循环液,接通加热搅拌电源,控制加热温度使回流量保持在1~2滴/s,稳定1 h,记录平衡温度;同时分别从汽相和液相取样口用微量注射器取样,采用气相色谱仪分析其组成;用注射器从沸腾室中取出2~3 mL釜液,然后加入同体积的纯的重组分物料,重新建立汽液相平衡。
1.5 实验装置的校验为了验证该汽液平衡装置的准确性和稳定性,使用该装置测定了乙醇+水二元体系的常压汽液平衡数据,并将实验结果与文献数据[6]比较,将乙醇+水二元体系汽液平衡数据的实验值和文献值做T-x-y图,结果如图 2所示。

|
| 图 2 乙醇(1)+水(2) 二元体系常压T-x-y相图 Figure 2 T-x-y plot of ethanol(1)+water(2) at at 101.3 kPa |
| |
由图 2可看出,测得的乙醇+水二元体系在常压下的汽液平衡数据与文献值吻合较好,表明该装置测定汽液平衡数据具有较好的稳定性和可靠性。
2 实验结果与数据处理 2.1 气相色谱的校正因子气相色谱的校正因子通过公式(1) 表示,其中A为气相色谱的峰面积、f为汽相色谱的校正因子、x为摩尔分数,下标1和2表示不同的组元。分析不同摩尔分数的二元体系混合物,以(A1/A2)为横坐标、以(x1/x2)为纵坐标作图,将数据做线性回归得到1条直线,直线的斜率即为(f1/f2)。由公式(2) 计算得到组分1的摩尔分数[7]。
| $ \frac{{{A_1}}}{{{A_2}}}\frac{{{f_1}}}{{{f_2}}} = \frac{{{x_1}}}{{{x_2}}} $ | (1) |
| $ {x_1} = \frac{{{A_1}{f_1}}}{{{A_2}{f_2}}}/\left( {1+\frac{{{A_1}{f_1}}}{{{A_2}{f_2}}}} \right) $ | (2) |
图 3为2, 2-二甲基丁烷(1)+乙醇(2) 二元体系校正因子图。图 4为2, 2-二甲基丁烷(1)+正丙醇(2) 二元体系校正因子图。

|
| 图 3 2, 2-二甲基丁烷(1)+乙醇(2) 二元体系的校正因子 Figure 3 The response factors of the binary systems 2, 2-dimethylbutane (1)+ethanol (2) |
| |

|
| 图 4 2, 2-二甲基丁烷(1)+正丙醇(2) 二元体系的校正因子 Figure 4 The response factors of the binary systems 2, 2-dimethylbutane (1)+1-propanol (2) at 101.3 kPa |
| |
由图 3和图 4可以看出,数据的线性关系很好。图 3直线的斜率为0.242,即2, 2-二甲基丁烷(1)+乙醇(2) 二元体系校正因子(f1/f2)=0.242。图 4直线的斜率为0.4862,即2, 2-二甲基丁烷(1)+正丙醇(2) 二元体系校正因子(f1/f2)=0.4862。
2.2 汽液平衡的测定结果2, 2-二甲基丁烷(1)+乙醇(2) 二元体系在常压下的汽液平衡数据的测定结果见表 2和图 5。当x1=0.8052时,2, 2-二甲基丁烷和乙醇形成二元共沸物,共沸点T=45.2 ℃。
| t/℃ | x1 | y1 | y1, cal | |△y1, cal| |
| 49.9 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0080 | 0.0080 |
| 48.4 | 0.9708 | 0.9473 | 0.9367 | 0.0106 |
| 46.8 | 0.9343 | 0.8949 | 0.8707 | 0.0241 |
| 45.6 | 0.8966 | 0.8355 | 0.8272 | 0.0083 |
| 45.2 | 0.8052 | 0.8041 | 0.8147 | 0.0106 |
| 45.6 | 0.6487 | 0.7974 | 0.8037 | 0.0063 |
| 45.9 | 0.5188 | 0.7932 | 0.8014 | 0.0082 |
| 46.2 | 0.3663 | 0.7879 | 0.7942 | 0.0063 |
| 47.3 | 0.2866 | 0.7639 | 0.7832 | 0.0193 |
| 49.7 | 0.1876 | 0.7291 | 0.7442 | 0.0151 |
| 51.3 | 0.1594 | 0.6946 | 0.7105 | 0.0159 |
| 52.0 | 0.1507 | 0.6742 | 0.7007 | 0.0264 |
| 53.4 | 0.1234 | 0.6495 | 0.6400 | 0.0094 |
| 54.7 | 0.1140 | 0.6278 | 0.6286 | 0.0008 |
| 55.6 | 0.1065 | 0.6087 | 0.6141 | 0.0054 |
| 56.3 | 0.1025 | 0.5972 | 0.6092 | 0.0120 |
| 57.0 | 0.0961 | 0.5768 | 0.5920 | 0.0152 |
| 57.9 | 0.0901 | 0.5566 | 0.5782 | 0.0216 |
| 59.4 | 0.0803 | 0.5276 | 0.5510 | 0.0234 |
| 60.1 | 0.0713 | 0.5194 | 0.5105 | 0.0089 |
| 61.2 | 0.0646 | 0.5002 | 0.4849 | 0.0153 |
| 62.6 | 0.0611 | 0.4663 | 0.4804 | 0.0141 |
| 63.3 | 0.0636 | 0.4489 | 0.4661 | 0.0172 |
| 64.3 | 0.0542 | 0.4206 | 0.4540 | 0.0334 |
| 65.5 | 0.0436 | 0.3881 | 0.3875 | 0.0006 |
| 66.2 | 0.0457 | 0.3691 | 0.4120 | 0.0429 |
| 67.3 | 0.0386 | 0.3491 | 0.3645 | 0.0154 |
| 68.0 | 0.0326 | 0.3222 | 0.3187 | 0.0035 |
| 69.2 | 0.0309 | 0.2988 | 0.3130 | 0.0143 |
| 70.0 | 0.0284 | 0.2647 | 0.2952 | 0.0305 |
| 70.7 | 0.0224 | 0.2452 | 0.2412 | 0.0040 |
| 71.6 | 0.0237 | 0.2189 | 0.2345 | 0.0156 |
| 73.3 | 0.0205 | 0.1699 | 0.2066 | 0.0367 |
| 74.5 | 0.0163 | 0.1455 | 0.1952 | 0.0497 |
| 75.2 | 0.0090 | 0.1201 | 0.1124 | 0.0077 |
| 75.9 | 0.0077 | 0.0810 | 0.0980 | 0.0170 |
| 76.7 | 0.0042 | 0.0646 | 0.0547 | 0.0099 |
| 77.2 | 0.0033 | 0.0414 | 0.0437 | 0.0023 |
| 78.5 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 |

|
| 图 5 2, 2-二甲基丁烷(1)-乙醇(2) 二元体系常压T-x-y相图 Figure 5 T-x-y plot of 2, 2-dimethylbutane(1)+ethanol(2) at at 101.3 kPa |
| |
2, 2-二甲基丁烷(1)+正丙醇(2) 二元体系在常压下的汽液平衡数据的测定结果见表 3和图 6。当x1=0.9218时,2, 2-二甲基丁烷和正丙醇形成二元共沸物,共沸点T=49.2 ℃。
| t/℃ | x1 | y1 | y1, cal | |△y1, cal| |
| 49.9 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 0.0000 |
| 49.7 | 0.9596 | 0.9420 | 0.9543 | 0.0123 |
| 49.2 | 0.9218 | 0.9249 | 0.9452 | 0.0203 |
| 49.4 | 0.8874 | 0.9201 | 0.9305 | 0.0104 |
| 49.8 | 0.8211 | 0.9178 | 0.9238 | 0.0060 |
| 50.8 | 0.6604 | 0.9050 | 0.9194 | 0.0144 |
| 52.1 | 0.5149 | 0.8903 | 0.9037 | 0.0134 |
| 53.7 | 0.3917 | 0.8803 | 0.8945 | 0.0142 |
| 54.3 | 0.3417 | 0.8758 | 0.8883 | 0.0125 |
| 55.3 | 0.3122 | 0.8649 | 0.8823 | 0.0174 |
| 56.3 | 0.2852 | 0.8567 | 0.8785 | 0.0218 |
| 58.5 | 0.2386 | 0.8351 | 0.8346 | 0.0005 |
| 60.1 | 0.2174 | 0.8201 | 0.8221 | 0.0020 |
| 62.9 | 0.1714 | 0.7677 | 0.7520 | 0.0157 |
| 64.7 | 0.1528 | 0.7430 | 0.7271 | 0.0159 |
| 65.7 | 0.1410 | 0.7226 | 0.7033 | 0.0192 |
| 67.1 | 0.1252 | 0.6911 | 0.6664 | 0.0247 |
| 68.1 | 0.1206 | 0.6801 | 0.6659 | 0.0142 |
| 69.4 | 0.1116 | 0.6670 | 0.6489 | 0.0181 |
| 71.7 | 0.0999 | 0.6421 | 0.6325 | 0.0096 |
| 73.2 | 0.0911 | 0.6213 | 0.6105 | 0.0108 |
| 74.8 | 0.0818 | 0.5899 | 0.5823 | 0.0076 |
| 77.2 | 0.0710 | 0.5525 | 0.5498 | 0.0027 |
| 78.5 | 0.0671 | 0.5342 | 0.5422 | 0.0080 |
| 80.0 | 0.0630 | 0.4990 | 0.5341 | 0.0351 |
| 81.1 | 0.0516 | 0.4735 | 0.4591 | 0.0144 |
| 82.7 | 0.0460 | 0.4354 | 0.4309 | 0.0046 |
| 84.4 | 0.0402 | 0.3856 | 0.3977 | 0.0122 |
| 85.7 | 0.0350 | 0.3487 | 0.3621 | 0.0134 |
| 87.3 | 0.0287 | 0.3125 | 0.3126 | 0.0001 |
| 88.9 | 0.0257 | 0.2684 | 0.2931 | 0.0247 |
| 90.5 | 0.0209 | 0.2268 | 0.2510 | 0.0242 |
| 92.0 | 0.0183 | 0.1725 | 0.2290 | 0.0564 |
| 93.4 | 0.0114 | 0.1278 | 0.1491 | 0.0213 |
| 95.0 | 0.0070 | 0.0810 | 0.0958 | 0.0148 |
| 96.0 | 0.0050 | 0.0566 | 0.0707 | 0.0141 |
| 97.4 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 |

|
| 图 6 2, 2-二甲基丁烷(1)-正丙醇(2) 二元体系常压T-x-y相图 Figure 6 T-x-y plot of 2, 2-dimethylbutane(1)+1-propanol (2) at at 101.3 kPa |
| |
常压下,汽相可以视为理想气体,汽液平衡关系式可以简化为公式(3)。
| $ p{y_i} = {p_i}^{\text{s}}{x_i}{\gamma _i} $ | (3) |
式(3) 中:p为系统压力;yi为组分i的汽相摩尔分数;pis为纯组分i在平衡温度下的饱和蒸汽压;xi为组分i的液相摩尔分数;γi为组分i液相的活度系数。2, 2-二甲基丁烷的pis由公式(4) 所示的Antoine方程计算[8],乙醇和正丙醇的pis由公式(5) 所示的Antoine方程计算[9]。
| $ {\text{ln}}{p^{\text{s}}} = A - \frac{B}{{T+C}} $ | (4) |
| $ {\text{lg}}{p^{\text{s}}} = A - \frac{B}{{T+C}} $ | (5) |
2, 2-二甲基丁烷、乙醇和正丙醇的Antoine系数见表 4。
| A | B | C | |
| 2, 2-二甲基丁烷 | 13.8874 | 2 668.868 | -34.868 |
| 乙醇 | 7.30243 | 1 630.868 | -43.569 |
| 正丙醇 | 6.97878 | 1 497.734 | -69.056 |
采用Herrington等推荐的面积检验法对实验得到的两组二元体系等压汽液平衡T-x-y数据进行热力学一致性检验。计算过程如下:
| $ I = \int\limits_0^1 {{\text{ln}}} \left( {\frac{{{\gamma _1}}}{{{\gamma _2}}}} \right){\text{d}}{x_1} $ | (6) |
| $ \sum { = \int\limits_0^1 {|{\text{ln}}\frac{{{\gamma _1}}}{{{\gamma _2}}}|{\text{d}}{x_1}} } $ | (7) |
| $ D = \frac{{|I|}}{{\sum {} }} \times 100 $ | (8) |
| $ J = 150 \times \frac{{{T_{\max }} - {T_{\min }}}}{{{T_{\min }}}} $ | (9) |
式(6)~(9) 中:γ1、γ2分别为组元1、组元2的液相活度系数;Tmax、Tmin分别为体系的最高、最低沸点。2组二元体系等压汽液平衡数据的热力学一致性检验结果见表 5。
| D | J | D-J | |
| 2, 2-二甲基丁烷+乙醇 | 0.0122 | 15.6903 | -15.6781 |
| 2, 2-二甲基丁烷+正丙醇 | 20.7412 | 21.5115 | -0.7703 |
由表 5可见,2组二元体系等压汽液平衡数据均满足D-J < 10,符合热力学一致性。
2.5 实验数据的关联NRTL方程[10]的适用范围很广,对于烃、醇、酮、醛、酸及水等的混合物均适用。二元体系的NRTL活度系数方程为:
| $ \ln {\gamma _1} = {x_2}^2\left[ {\frac{{{\tau _{21}}{G_{21}}^2}}{{{{({x_1}+{x_2}{G_{21}})}^2}}}+\frac{{{\tau _{12}}{G_{12}}}}{{{{({x_2}+{x_1}{G_{12}})}^2}}}} \right] $ | (10) |
| $ \ln {\gamma _2} = {x_1}^2\left[ {\frac{{{\tau _{12}}{G_{12}}^2}}{{{{({x_2}+{x_1}{G_{12}})}^2}}}+\frac{{{\tau _{21}}{G_{21}}}}{{{{({x_1}+{x_2}{G_{21}})}^2}}}} \right] $ | (11) |
| $ {\tau _{21}} = \frac{{{g_{21}} - {g_{11}}}}{{RT}},{\tau _{12}} = \frac{{{g_{12}} - {g_{22}}}}{{RT}} $ | (12) |
式(10)~(12) 中G21=exp(-α12τ21),G12=exp(-α12τ12)。α12是组元1和组元2之间的参数,称为非随机参数。(g21-g11)/R、(g12-g22)/R和α12是NRTL方程参数。
利用Aspen Plus的Data Regression功能,得到NRTL模型参数如表 6所示,并由模型方程计算出每个二元体系的汽相组成y1, cal,并计算y1的计算值和实验值的偏差,如表 2和表 3所示。
| α12 | (g12-g22)/R | (g21-g11)/R | |
| 2, 2-二甲基丁烷+乙醇 | 0.3 | 810.492 | 1 833.400 |
| 2, 2-二甲基丁烷+正丙醇 | 0.3 | 2 856.218 | 225.921 |
y1的平均偏差:
汽相组成的平均偏差小于0.02,可以看出实验数据和计算数据吻合很好,说明NRTL方程适用于该二元体系。
3 结论1) 实验测定了常压下2, 2-二甲基丁烷+乙醇和2, 2-二甲基丁烷+正丙醇二元体系的汽液平衡数据。并对实验数据进行了Herington面积法检验,结果表明两组数据均符合热力学一致性。
2) 对2组常压汽液平衡数据用NRTL方程进行关联,得到了相应的模型参数。利用得到的模型参数计算汽相物质的量组成,实验值与计算值吻合良好,说明NRTL模型适用于所研究的二元体系。
| [1] |
王宏亮, 邵生富, 徐芸, 等. 甲基亚膦酸二乙酯的合成工艺研究[J].
精细化工中间体, 2005, 35(2): 54–56.
Wang Hongliang, Shao Shengfu, Xu Yun, et al. Studies on the synthetic process of diethyl methyl-phosphonite-intermediate of glufosinate[J]. Fine Chemical Intermediates, 2005, 35(2): 54–56. |
| [2] | Aucejo A, Loras S, Muñoz R, et al. Isobaric vapor-liquid equilibrium for binary mixtures of 2-methylpentane+ethanol and+2-methyl-2-propanol[J]. Fluid Phase Equilibria, 1999, 156(1): 173–183. |
| [3] | Pokki J P, Uusi-Kyyny P, Aittamaa J, et al. Vapor-Liquid equilibrium for the 2-methylpentane+2-methyl-2-propanol and+2-butanol systems at 329 K[J]. Journal of Chemical & Engineering Data, 2002, 47(2): 371–375. |
| [4] | Gabaldón C, Martínez-Soria V, Marzal P, et al. Isobaric vapor-liquid equilibria for the binary system 3-methylpentane+ethanol and for the ternary system 2-methyl-2-propanol+ethanol+3-methylpentane at 101.3 kPa[J]. Journal of Chemical & Engineering Data, 2000, 45(5): 882–886. |
| [5] | Uusi-Kyyny P, Pokki J P, Aittamaa J, et al. Vapor-Liquid equilibrium for the binary systems of 3-methylpentane+2-methyl-2-propanol at 331 K and+2-butanol at 331 K[J]. Journal of Chemical & Engineering Data, 2001, 46(3): 754–758. |
| [6] | Gmehling J, Onken U. Vapor-Liquid equilibrium data collection. DECHEMA chemistry data series[J]. Frankfurt, 1977, 1(1): 127–157. |
| [7] | Pokki J, Rehak K, Kim Y, et al. Vapor-Liquid equilibrium data at 343 K and excess molar enthalpy data at 298 K for the binary systems of ethanol+2, 4, 4-trimethyl-1-pentene and 2-propanol+2, 4, 4-trimethyl-1-pentene[J]. Journal of Chemical & Engineering Data, 2003, 48(1): 75–80. |
| [8] | Garriga R, Pérez P, Valero J, et al. Vapour pressures at several temperatures and excess functions of n-butanol with 2, 2-dimethylbutane and with 2, 3-dimethylbutane at 298.15 K[J]. Fluid Phase Equilibria, 1994, 102(1): 85–95. DOI: 10.1016/0378-3812(94)87092-6 |
| [9] | 马沛生, 李永红. 化工热力学[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2009 |
| [10] | Renon H, Prausnitz J M. Local compositions in thermodynamic excess functions for liquid mixtures[J]. AIChE Journal, 1968, 14(1): 135–144. DOI: 10.1002/(ISSN)1547-5905 |
 2017, Vol. 34
2017, Vol. 34